How to make the decision to invest in early-stage start-ups as a private investor
My investment decision-making process in three early-stage investment opportunities

1. Introduction
Research shows that private investors are crucial in the early stage of investments. Venture Capitalists often only invest in start-ups which have obtained an early-stage investment.
But how do private investors make their decision in investing in early-stage start-up? In this article, I will analyse my decision-making process as a Co-Investor in the early-stage investment Syndicate Room platform to invest in three real investment cases. I show how to approach an investment decision, and the tools and techniques I use to guide my analysis and decision making.

In this investment cases, my primary goal is to maximise my ROI over a period of five years.
I will make an Enterprise Investment Scheme (EIS) investment of £100,000 in three early-stage investment opportunities: TC Biopharm, Mayku, Digital Therapeutics.
In this article, I will first outlay the assessment criteria, second evaluate the proposals in terms of the criteria and show my primary concerns, analyse what further data and information is needed to make a proper decision, and third finalise my investment decision in a recommendation.
2. Decision tools and techniques
As a Business Angels, I will use a shortcut decision making heuristic known as elimination-by-aspects theorised by Maxwell et al.¹ to reduce the available investment opportunities. I demonstrated the limitation of the theory and developed it further by incorporating the tools and techniques learned through previous investments.
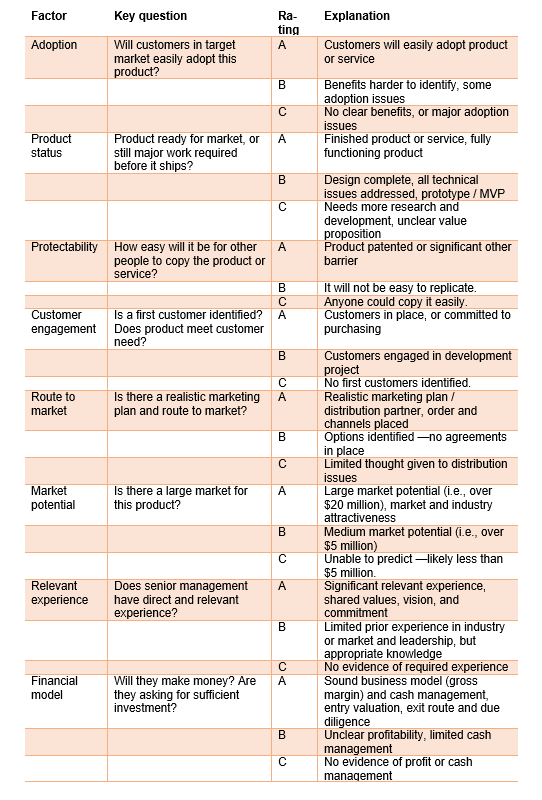
The decision-making tool has the advantages of being a fast-decision-making tool. It is a non-compensatory decision-making heuristic. The decision-making tool is based on the assumption that if an opportunity is diagnosed with a fatal flaw (rating: C), it is rejected in the first stage of the decision-making process. The model uses a comprehensive approach to assess the proposals across a set of eight critical factors (key question and explanation).
In the following I will outlay a summary of the investment decision, my primary concern and the further data and information I would need to make a final decision to fund the proposal.
Practical research showed that an elimination-by-aspects decision making heuristic is not used for the final funding decision. Instead, other criteria, more subjective are used to make the final decision. This I will show which data is needed to make a more informed decision.
I developed the model further as the critical factors have limitations. Some factors might not have been considered in the model or some are unnecessary (industry attractiveness).
The eight factors are adoption, product status, protectability, customer engagement, route to market, market potential, relevant experience, and financial model.
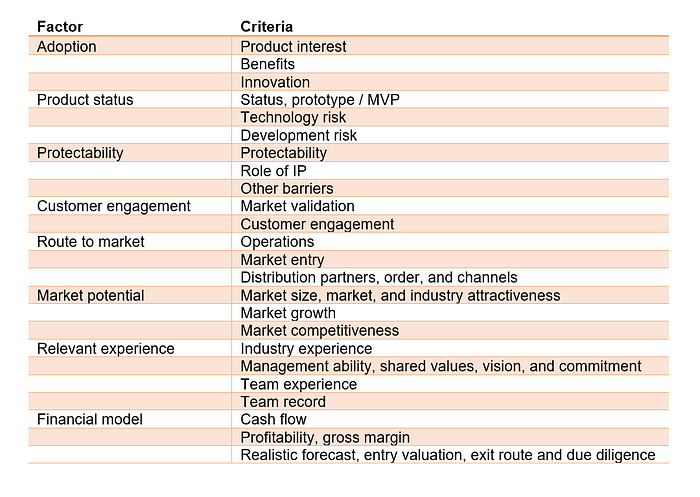
The second factor product status assesses if the product is market ready across status, technology risk and development risk. I should be further detailed by indicators such as clear value proposition, prototype / MVP, and fully functioning product.⁴
The fifth key criterion is route to market. This assesses if the route to market is realistic in terms of operations, market entry and distribution partners. Useful additional categories include order and channels as well as the marketing machine.⁵
The sixth criterion is market potential. It assesses if the market is large enough for product across market size, market growth and market competitiveness. The category can be better assessed by two other factors, market attractiveness and the wider industry attractiveness.⁶
Seventh factor is relevant experience of senior management. It comprises industry experience, management ability, team experience and team record. For a better understanding, founders, team, operations, and culture⁷ as well as shared values, vision and commitment and prior experience in this industry or market and leadership should be additionally assessed.
The eights factor is financial model. It measures whether the business model is profitable, and investment are secured. This includes cash flow, profitability, and realistic forecast. Factors such as gross margin, entry valuation, exit route and due diligence complete the assessment.⁸
3. Proposal evaluation
In the following, I will evaluate the three proposals according to their strength and weaknesses, primary concerns, and further data and information needed to make a final investment decision.
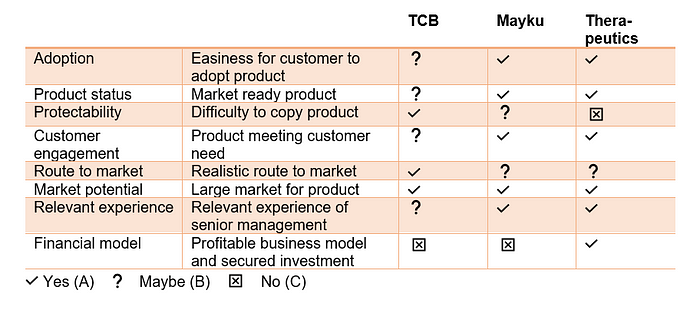
In summary, I used the elimination-by-aspects decision making heuristic by Maxwell et al. reduce the available investment opportunities. I came to the decision to not invest in any of the proposals because each of these has a primary concern or fatal flaw (rating: C).
In every case further assessment via additional data and information is needed because all three investment cases span different industries and products. TC Biopharm Limited (TCB) has developed a clinical therapy called ImmuniCell which harnesses the body’s own immune system to fight cancerous tumours. Mayku has created a tabletop machines FormBox to help makers “do it yourself”. Digital Therapeutics developed a cost-effective, evidence-based digital therapeutic interventions App, Quit Genius, aims to address the rising cost of preventable chronic diseases like smoking.
3.1 TC Biopharm

3.1.1 Strengths and weaknesses
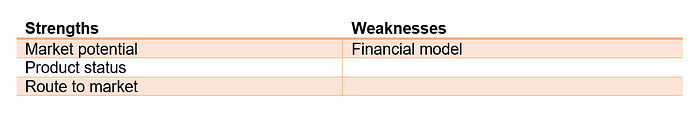
The strength of TCB are in the big oncology markets, the late stage clinical trial they have achieved and the pipeline they established with regulatory bodies.
The start-ups’ weaknesses are in the field of cost and revenues. There is no indication about the costs (only stated that it would be lighter as compared to genetic competitors) and price. Also, competitors might threaten if they lose their first mover advantage.
Market potential
There is a large market potential with over $20 million: TCB has a large addressable market and based on independently prepared information, estimates annual EU revenues of between £100m and £500m five years post launch. The market size is big, the market growth is expected to be high. The initial addressable market is expected to be 65,000 patients at launch for lung cancer, kidney cancer, melanoma. They expect the increase the addressable market year on year. The market competitiveness is still low.
Product status
The product is not ready for market yet but there is still work required before it launches. The design is complete all technical issues addressed Y. But the product needs more research and development. The product status is still late stage with Phase II/III clinical asset. Whereas the technology risk is low the development risk is very high. There are two main elements of risk: clinical and commercial. Both risk are being mitigated. In summary, the product is not market ready yet.
Adoption
In general, it is hard for customers to adopt to the product, but this product has a good pipeline. It is difficult to get into clinics, but the end customer will adopt the product easily because they need treatment. The product interest at clinics and cancer patients is high. The benefits for cancer patients are also high: ImmuniCell represents a benefit for payers and health authorities over current standards of care due to enhanced clinical benefit and a potentially significant reduction in adverse events. The extend of innovation of cancer patients is also high.
Protectability
It is difficult to copy the product. The product will be patented or significant other barrier. The product Immunicell is IP protected. In addition, the pipeline project are protected, too. There are significant other barriers to entry for other companies to move into the space. There are also couple intellectual properties. In addition, there are knowhow and relationships with consultants.
Customer engagement
There is a first customer identified and product meets customer need.
The customers in place and committed to purchasing as well as customers engage in development project Y. There is a market validation and customer engagement via Y trial. The regulatory body approved product MHRA. The end customers are cancer patients, but the product is sold through clinicians and medical oncologists. There is a lot of interest in UK but also Netherland is interested join study.
Route to market
There is a realistic marketing plan and distribution partner in place. The operations are in place, the market entry is prepared, and distribution partners are engaged. The options are identified. ImmuniCell represents a benefit for payers and health authorities over current standards of care due to enhanced clinical benefit. TCB is actively engaging with clinicians to ensure significant uptake through clinical studies and beyond and has established a dialogue with payment bodies.
Relevant experience
The senior management has direct and relevant experience: The CEO and leadership team has industry experience, long year management ability. The team experience and the team record are good. The CEO has 30 years’ experience in regenerative medicine, during which he progressed 10 different cell-based products from the laboratory into clinic. The other senior management, too.
Financial model
One can expect that they will make money with a profitable business model, but did they secure sufficient investment. The profitability is unclear so far: there is no information about cash flow, profitability and not stated a realistic forecast. The Pre-money valuation £8,000,000. And they have funds via one raise from Narec Capital of £711,000. They are using this fund to go from clinical A trials dosage and then over into stage 2b. TCB anticipates a public listing on Nasdaq in H1, 2018. This strategy is being executed in conjunction with the Company’s lead financial advisor, Narec Capital Limited. In general, it is a high risk, high reward market.⁹
3.1.2 Primary concern
My primary concern are costs and revenues, which are not clearly stated. I would expect high R&D costs. On the other side I am concerned because I would have expected the clinical trials be more advance in 2020 but there still in Phase II/III. Another concern is that they have not achieved an IPO in 2018 yet other than stated in their Syndicate Room pitch.¹⁰
3.1.3 Further data and information
I would need further data and information in order to make my final decision are cost, revenues and price to assess if this is a profitable business. Further competitor data about how the advanced in immunotherapy medicine. Further data about their current trial phase and further information when they plan to launch. I would also like to know why they have not achieved an IPO in 2018 yet.
3.1.4 Conclusion
In total, I do decide to invest in this company. Significant for my decision is that they have attracted other investors and did further trials until 2020.
3.2 Mayku

3.2.1 Strengths and weaknesses
The strength of Mayku is their addressable market, the current sold products.
On the contrary the company’s weaknesses are their financial model, specifically the high product price and flaws in the route to market via on-sale products.
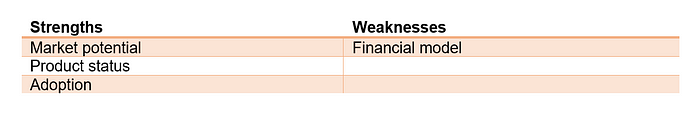
Adoption
Customers easily adopted the product. The product interest is in general high: Mayku have already sold to more than 3,000 people in 74 countries and the number keeps growing. These sales led to £1.2m in revenue for 2018. 700% sales growth since July monthly sales. The benefits are good. Customers include Nike, NASA, Nestlé and other large enterprise customers as well as schools, chocolatiers, craft businesses and families. They have an impressive corporate client list already using their products. Innovation is high because it is the first of its kind. They had a Kickstarter campaign where 1,745 backers pledged $588,775.
Product status
The product is ready for market. It is a finished product and already sold.
In addition, in 2020 Mayku plan to launch a more affordable FormBox. They plan to create an integrated tabletop factory of in total three products. They are planning to add to tabletop products an ecosystem of consumables etc where tabletop is only the gateway to consumables, material of kits, downloads, online classes. By helping is customers making beautiful content, the encourage further purchases by PR Paid Social Organic and therefore gain more customers. In addition, the technology risk and development risk are low.
Protectability
It will not be relatively easy to replicate now because the product is still considered new to the market. The alternatives are far more costly and time consuming to produce the same result. But in the long run there will be competitor products. In general, the protectability is not so high because it is lacking IP or other sunk cost barriers
Customer engagement
A first customer is in place and sales are made. The have already validate the product on the market and customers are engaged. Customers include Nike, NASA, Nestlé and other large enterprise customers as well as schools, chocolatiers, craft businesses and families. Customers to date include families, schools, chocolatiers, craft businesses and even large enterprise customers. Industries they serve span culinary, education, industry, craft and even PPE Masks.
Route to market
There is a realistic marketing plan and route to market in place. Whereas the route to market in terms of operations already in place. The product is made in China, to keep costs low. The market entry has already been made with their “low-cost” product. But distribution partners are not disclosed in the information.
The marketing plans spans options identified. By helping is customers making beautiful content, the encourage further purchases by PR Paid Social Organic and therefore gain more customers.
Market potential
In terms of the market size, here might be a large (over $20 million) to medium market (over $5 million) for this product but they have not stated it explicitly. They have already achieved £1.2m in revenue in 2018. But they are only stating that 35 million people in the US are spending 5 hours per week crafting. One of their store chains, Michaels, which serves just the service craft market has 1,300 stores, 5 billion $ and 20 million views on their online marketplace.
Relevant experience
The senior management has significant relevant experience. The team has experience across the board with all areas covered, with several members having previous entrepreneurial experience: CEO and business partner has experience in product development and marketing expert marketing in the craft industry. Specifically, the CPO has relevant industry experience in hardware design. The management ability might be medium.
Financial model
Their business model and cash management does not seem to be sound in terms of costs. In general, the profitability is good because they have 156 £ in cost per product, whereas they are making an indirect 50% profit margin at a 350 £ wholesales price or 70% margin with direct sales at 599 £.¹¹ They have not stated explicitly their forecast and costs are too high. They secured for sufficient investment. They opened a funding round in 2018 and where overfunded by 40% to their 1 million £ target. They have renowned investors such as Robert Devereux, Simon Murdoch and Chris Marks.
3.2.2 Primary concern
My primary concern with Mayku are their high cost and prices. In addition to the above-mentioned hardware prices for the product itself their business model relies on the assumption of up- and cross-sales as well as sales acceleration in an exosystem of product. But for example, their additional products are charged too high such as Mayku Cast Sheets £34.00 GBP or Mayku Form Sheets 30 pack £34.00 GBP.¹²
3.2.3 Further data and information
For further assessment of the investment, I need to do the full customer segmentation to further analyse profit margins and customer needs across the different market segment. In addition, I need further information and data about current and future purchasing ways and distribution partners to make proper decision. Lastly, the profit margin seems to be high for a commodity product. Therefore, I would need a further split into different customers and industries margins, benchmarked against competitors.
3.2.4 Conclusion
With regards to investing in Mayku, I do not make a favourable decision because of my primary concern of the high hardware and additional cost prices of the machine.
3.3 Quit Genius

3.3.1 Strengths and weaknesses
The main strength of Quit Genius is its large addressable market in health care, its product status which is already launched.
The most pressing weaknesses are its financial model, in particular its high prices.
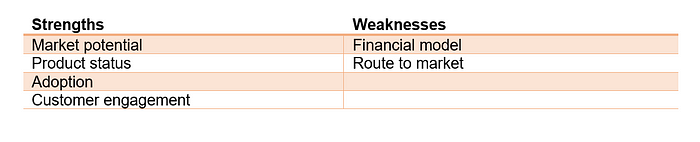
Adoption
Customers will easily adopt product: Digital Therapeutics is backed by Merck & Co and Telefonica, the Quit Genius app has been accessed by 9,510 users, and the company has been featured in a number of global media outlets. The product creates interest. It provides benefits. Because of its digital nature it is very innovative.
Product status
It is a finished product. Across the four-stage programme, smokers engage daily with a mix of animated video clips, audio sessions, interactive exercises, quizzes, and a range of evidence-based mindfulness exercises. The product status is market ready. There are pilot partnerships with large health insurers (8 months) established and it is directly publicly released.¹³
Protectability
I will be relatively easy to replicate. The protectability is low because there is no IP or other entry barriers.
Nonetheless it is a differentiated offering against competitor smoking apps: Competitor apps are often not evidence-based, counterintuitive, and only a component of science. The product contains a four-stage program across different media.
Customer engagement
Customers are in place and committed to purchasing. Quit Genius’ end users are individuals looking to quit smoking, who own a smartphone and are familiar with the process of downloading apps. The company’s B2B customers can be divided into the following three categories.
Route to market
There is a realistic marketing plan and route to market in place. The realistic marketing plan comprises a consumer growth strategy via a focus on organic acquisition through content marketing and SEO efforts. The market entry is made by current marketing via organic and world of mouth and press articles. With regards to operations there is no information. Instead, the distribution partnesr are in place.
Market potential
It seems that there is a large market for this product (over $20 million) but it is not clearly stated. Digital Therapeutics’ first product, Quit Genius, seeks to address the largest cause of preventable morbidity and premature mortality worldwide: smoking. Tobacco use results in nearly 6m deaths per year worldwide, predicted to rise to more than 8m by 2030. Market growth can be achieved by geographical expansion but is not clearly stated.
Relevant experience
The senior management has direct and relevant industry experience because the digital Therapeutics’ management team boasts three qualified doctors from Imperial College London. CEO and COO are experienced in founding companies. Their management ability is not stated. There is no further information about team experience or team record.
Financial model
In general, they have a sound business model and cash management in place, but prices seem to be too high, and revenues are not stated.
With regards to cash flow, they have in 2017 raised £400k from Angels and SyndicateRoom at a £1.56m pre-money valuation. In 2020 investors comprise Combinator, Village, SemperVirens, Octopus Ventures.¹⁴ Their profitability is not stated but revenues seem to be high and used in the industry. Their revenue model for consumers and businesses is a monthly subscription fee priced at £15 per user per month. For healthcare payer partners. But they have not stated a realistic forecast.
3.3.2 Primary concern
My primary concern with Quit Genius is their high prices and high costs. They have not stated a proper forecast of their returns. Despite the good financial investments, this makes them a risky player to invest in.
3.3.3 Further data and information
To better assess the investment, I need further price points of competitors and the payment willingness of their customers. I would also like to investigate further on their route to market and if they have secured further partners yet.
3.3.4 Conclusion
In terms of this short investment analysis, I am not likely to make an investment decision, despite the big market size of digital healthcare and the app-based product because of the high prices associated with.
4. Recommendation and conclusion
To sum up and to make the point, I recommend not to invest in any of the business because according to the decision by elimination heuristic each of these start-ups has some flaws. Further data and information are needed to make a proper final decision.
5. References
[1] Maxwell, Andrew & Jeffrey, Scott & Lévesque, Moren. (2011). Business Angel Early Stage Decision Making. Journal of Business Venturing. 26. 212–225
[2] Maxwell, Andrew & Jeffrey, Scott & Lévesque, Moren. (2011). Business Angel Early Stage Decision Making. Journal of Business Venturing. 26. 212–225
[3] Maxwell, Andrew & Jeffrey, Scott & Lévesque, Moren. (2011). Business Angel Early Stage Decision Making. Journal of Business Venturing. 26. 212–225
[4] The entrepreneur’s journey, Stage Model
[5] The entrepreneur’s journey, Stage Model
[6] The ‘Seven Domain’ model — (Mullins, 2018)
[7] The entrepreneur’s journey, Stage Model
[8] What VCs say they look for…
[9] TC Biopharm interview
[10] TC Biopharm (2020) Webiste. Retrieved from https://www.tcbiopharm.com/
[11] Mayku interview
[12] Mayku (2020) Webiste. Retrieved from https://www.mayku.me/
[13] Digital Therapeutics interview
[14] Quit Genius (2020) Webiste. Retrieved from https://www.quitgenius.com/
Thanks for reading! Liked the author?
If you’re keen to read more of my Leadership Series writing, you’ll find all articles of this weekly newsletter here.